Eye Surgical Treatments in Kolkata:
LASIK, Cataract and more
Spectra Eye Hospital in Kolkata helps people see better. We fix eye problems like blurry vision and eye pain. Our doctors use safe tools to treat eyes. We do surgeries like LASIK and cataract removal. LASIK helps you see without glasses. Cataract surgery clears cloudy vision. We also treat squint, glaucoma, and other eye issues. Our hospital is clean and staff are kind. We care for kids and adults. Come to us for healthy eyes. We want you to see the world clearly.We provide several eye surgeries to improve vision and eye health.
LASIK Surgery
LASIK is a laser surgery that corrects vision problems like nearsightedness. It reshapes the cornea to help you see clearly without glasses. Our hospital offers the best laser eye treatment in Kolkata.
Vitreoretinal Surgery
This surgery treats problems in the back part of the eye, like retinal detachment. Our specialists carefully repair the retina to restore vision.
Squint Surgery
Squint, or crossed eyes, can affect appearance and vision. Our surgeons adjust the eye muscles to align the eyes properly. This improves both look and sight.
Dacryocystorhinostomy
This procedure creates a new pathway for tears to drain when the tear duct is blocked. It helps prevent watery eyes and infections.
Entropion Surgery
Entropion causes the eyelid to turn inward, irritating the eye. Our surgery corrects the eyelid position, relieving discomfort.
Ectropion Surgery
Ectropion makes the eyelid turn outward, leading to dryness. We adjust the eyelid to its normal position to protect the eye.
Ptosis Surgery
Ptosis is a drooping upper eyelid that can block vision. Our surgeons lift the eyelid to improve sight and appearance.
LASIK Surgery in Kolkata: Achieve Clear Vision Without Glasses
Do you struggle with blurry vision or depend on glasses every day?
At Spectra Eye Hospital in Kolkata, we offer safe and advanced laser eye treatment and LASIK surgery. Our goal is to help people see clearly without needing glasses or lenses. If you are between 18 and 45 and have problems like near sightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism, our services might be the right choice.
Spectra Eye Hospital uses advanced laser machines and follows high safety standards. Our doctors have years of experience in eye care. They give each patient the right advice and best care. The treatment is quick, painless, and gives long-lasting results. Many people who visit us leave with better vision and a big smile. Laser surgery is not just about better eyesight. It also brings freedom and comfort in daily life. We offer the best laser eye treatment Kolkata. It helps you see clear without glasses.
Our expert Lasik surgeon in Kolkata check your eyes with care. We use safe tools for every step. You get full support during your visit. Come to us and choose the best Laser Eye Treatment Kolkata today.

What Is LASIK Surgery?
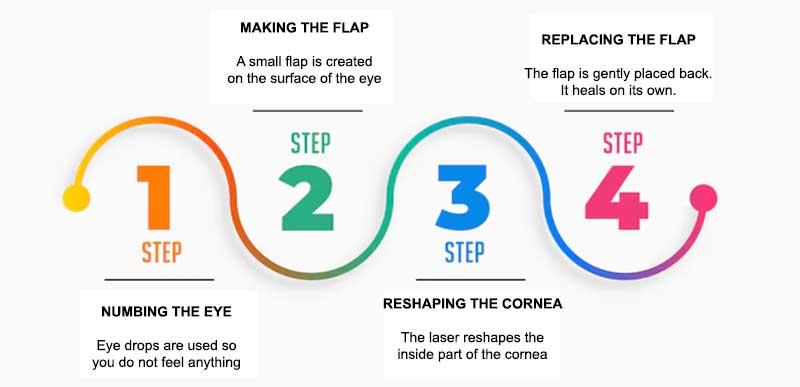
LASIK stands for Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis. It is a common eye surgery. It helps people with poor eyesight see better. The process uses a special laser to change the shape of the cornea. This allows light to hit the retina the right way. As a result, you see clearly.The LASIK surgery is very short. It usually takes about 15 minutes for both eyes. The doctor first gives numbing drops. Then, a thin flap is made on the surface of the eye. The laser then reshapes the cornea. After that, the flap is put back in place. The eye heals on its own. Most people do not feel any pain. And many start seeing better the next day.
LASIK surgery in Kolkata helps fix weak eyes. It uses safe light to change the eye shape. This makes far or near things look clear. Spectra Eye Hospital does this with care. You feel better and see well fast. Many people trust this place for good eye results.
LASIK helps fix many types of vision problems. This includes nearsightedness (trouble seeing far), farsightedness (trouble seeing close), and astigmatism (blurry vision).
Why Choose Spectra Eye Hospital for Best Laser Eye Treatment in Kolkata?
- Experienced Doctors: Our doctors have done many laser eye surgeries. They know how to handle every patient with care.
- Modern Technology: We use the latest laser machines. This helps make treatment fast and safe.
- Affordable Pricing: We believe good eye care should not be costly. Our prices are fair and clear.
- Friendly Staff: Our team is kind and helpful. From your first visit to the last, we are here to guide you.
- Convenient Locations: We have clinics at Chinar Park and Madhyamgram. You can choose the one nearest to you.
- High Patient Satisfaction: Most of our patients are happy with their results. Many recommend us to their friends and family.
Types of Laser Eye Treatments We Offer
At Spectra Eye Hospital, we offer safe laser eye treatments. Each treatment is done by our expert team, including the best LASIK surgeon in Kolkata. We help you choose what is right for your eyes.LASIK - LASIK is the most common laser treatment. It is quick and safe. It helps fix nearsightedness and farsightedness. A small flap is made and shaped.
PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy) - PRK is good for people with thin corneas. It does not use a flap. The surface of the eye is shaped to fix vision.
SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction) - SMILE is a newer and gentle method. A small piece is removed through a tiny cut. It causes less dryness and heals fast.
LASEK (Laser-Assisted Sub-Epithelial Keratectomy) - LASEK is a mix of PRK and LASIK. It is used if LASIK is not the right choice. It is safe and helps many people.
At Spectra Eye Hospital, our team checks your eyes first. Then, we suggest the best treatment for your needs. Our best LASIK surgeon in Kolkata will guide you with care.
We use the latest tools and methods. You get the best results and full support at every step. Come visit us to learn more and improve your vision.
How Does the LASIK Procedure Work?
Benefits of Laser Eye Surgery
- Clear Vision: Most people get 20/20 vision or even better.
- Fast Recovery: You can go back to work the next day.
- Safe: LASIK has a high success rate with very few side effects.
- Long-Term Results: The change in vision is often permanent.
- No More Glasses: You can enjoy life without glasses or contact lenses.
Call us at +91-8420596024 or email info@spectraeyehospital.com to schedule your visit.
You can also fill out the form on our website.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- Eye surgical treatments fix eye problems. Doctors use tools to treat the eyes. These can help you see better. Some treat cloudy eyes or weak eye muscles.
- Yes, it is safe at Spectra Eye Hospital. The doctors have good training and use clean tools. They check your eyes before they do any work.
- People with eye pain or low sight need help. Some have blurry vision or eye injury. The doctors at Spectra Eye Hospital can treat these well.
- A device keeps your eye open. The laser also stops if you move.
- You must be over 18, have stable vision, and no major eye issues.
- Most people do not need glasses after surgery. Some may need them later in life for reading.
- You can get the best Laser eye treatment in Kolkata at Spectra Eye Clinic. Our doctors use new tools and care. We help you see well with no pain. You can book your test and get help fast.
- LASIK surgery in Kolkata is safe and fast. Our doctor checks if your eyes are ready. It takes a few minutes to fix vision. Most people see clearly the next day. Our team gives full care and support.
- The best LASIK surgeon in Kolkata works at Spectra Eye Clinic. Many people trust our doctor for clear sight. You meet the surgeon before your surgery starts. We explain the steps in simple words to you.
- Yes, the best Laser eye treatment in Kolkata can fix weak eyes. It shapes the eye to see better. Most people stop using glasses after surgery. You get full help from our team before and after.
- You can meet the best LASIK surgeon in Kolkata at Spectra Eye Clinic. Book a test to check your eyes. Our doctor will guide you step by step. The visit is easy and does not take long.
- Call +91-8420596024 or visit spectraeyehospital.com to book.
